Should Children Eat a Carnivore Diet?


Navigating the world of nutrition for children can be a complex task, especially in today’s health-conscious society. As the popularity of the carnivore diet surges among adults for its health benefits, a common and pressing question arises: Is this diet suitable for children? This topic ranks as one of our most frequently asked questions, reflecting a growing curiosity and concern among parents.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of a meat-heavy, low-carb diet for children. While a strict carnivore diet is uncommon and generally not recommended for young ones, incorporating a diet rich in high-quality meats can offer significant nutritional benefits. However, it’s crucial to understand the balance and the specific needs of growing children.
Our aim is to provide clear, well-researched insights into this nuanced dietary approach. We’ll delve into the pros and cons, backed by scientific understanding and practical wisdom, to help parents make informed and healthful decisions for their children’s nutrition and overall well-being.
What Is the Carnivore Diet?
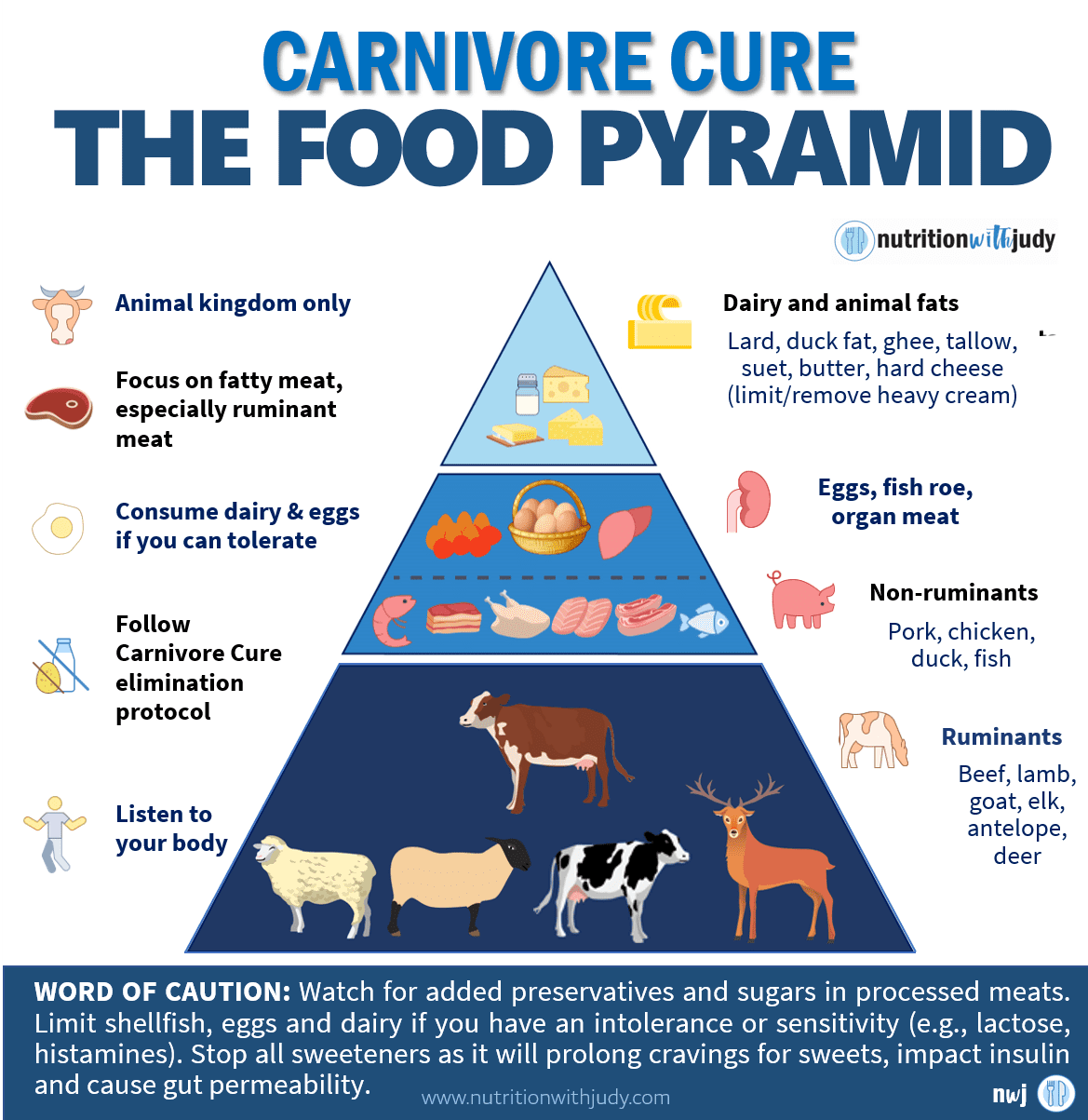

The carnivore diet, fundamentally, is a regimen that involves consuming primarily animal products. It’s a restrictive diet that focuses on animal foods, and can include animal products such as eggs and certain dairy items, eliminating other food groups. This diet is gaining attention for its compelling health benefits, such as weight loss, improved digestion, and reduced inflammation. There are several variations of the carnivore diet, each with its unique focus:
- Beef-Only Carnivore Diet: This variant restricts the diet to only beef, salt, and water. It’s chosen for its simplicity and is often used as an elimination diet to identify food sensitivities. It’s also the ideal place to start for highly sensitive individuals who are looking to support autoimmunity and gut healing.
- Lion Diet: A more restrictive version, the lion diet consists of ruminant meats (beef, lamb, elk, bison, goat, and so on), salt, and water only. With a bit more variety than beef-only, the lion diet is also a great place to start for individuals looking for more significant dietary support.
- Nose-to-Tail Carnivore Diet: This approach includes a variety of animal products, including organ meats and bone broths, to ensure a more comprehensive nutrient intake. We always recommend eating organs in proportion to the rest of the animal in order to avoid the risk of vitamin A toxicity from the overconsumption of certain organ meats such as liver and kidney. Nose-to-tail can be great for certain scenarios where individuals are targeting specific nutritional deficiencies, thyroid conditions, and more.
- Zero-Carb Carnivore Diet: As the name suggests, this variant excludes all carbohydrate sources, focusing solely on animal products. In this version of the carnivore diet, eggs and dairy are also included. While eggs and dairy technically do have minimal carb content, this way of eating is nearly zero-carb.
- Carnivore Keto Diet: This version combines principles of the ketogenic and carnivore diets, emphasizing high-fat, moderate-protein animal products while keeping carbohydrate intake minimal. It includes a bit more food freedom with vegetables that are considered lower toxicity in terms of plant anti-nutrients and pesticide exposure. This diet is often recommended for metabolically healthy individuals such as children.
- Carnivore-ish Keto Diet: A less restrictive form, this includes some plant-based foods such as low-carb vegetables and nut products, along with a focus on animal products. This diet is also recommended for metabolically healthy individuals including children.
- Animal-Based Diet: This variant sports meat, organs, raw dairy, fruit, and honey. In our clinical practice, we’ve only seen individuals who are elite athletes or are metabolically healthy and flexible do well on this type of diet. If you are athletic, metabolically healthy, and don’t struggle with sugar or food addiction, this could be an option to explore.
Each variation of the carnivore diet caters to different health goals and personal preferences, with some being more restrictive than others. It’s important for individuals to consult with their trusted healthcare provider before starting any new diet, especially those with specific health conditions or dietary needs.
What Are the Benefits of the Carnivore Diet?
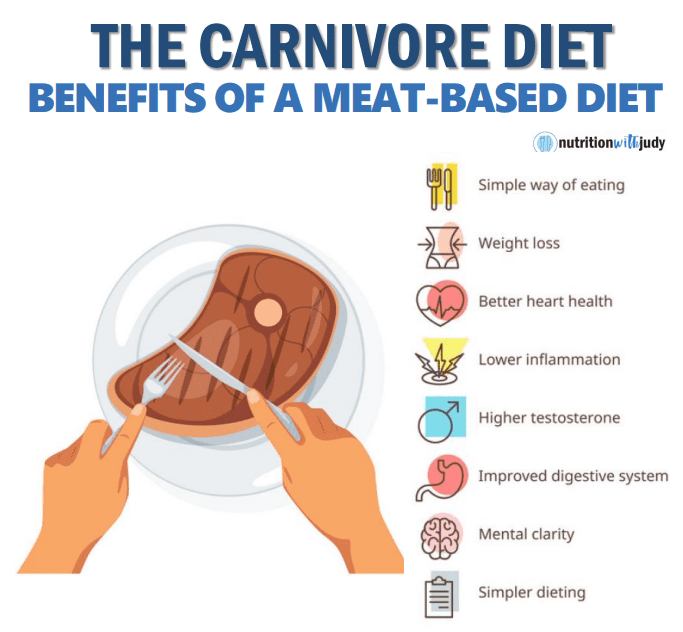

1. Simplified Nutrition: The carnivore diet simplifies eating by focusing solely on animal products. This can make meal planning and grocery shopping more straightforward, as the choices are limited by which diet variation you choose.
2. Weight Loss: Many individuals find that they lose weight on the carnivore diet. This is often due to a reduction in empty calorie intake and the high satiety levels of protein and fat, which can lead to a natural reduction in food consumption.
3. Improved Digestive Health: Without the fiber, carbohydrates, and anti-nutrients from certain plant-based foods, many people report an improvement in digestive issues. The carnivore diet can be particularly beneficial for those with conditions such as IBS or bloating, as it reduces fermentable carbohydrates.
4. Blood Sugar Control: The absence of carbohydrates on the carnivore diet can lead to more stable blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for people with diabetes or metabolic syndrome. It eliminates spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels that are often caused by carbohydrate consumption.
5. Mental Clarity and Energy Levels: Many adherents of the carnivore diet report enhanced mental clarity and increased energy levels. This could be due to the elimination of sugar and processed foods, which can cause fluctuations in energy and mood.
6. Reduced Inflammation: Animal-based foods are generally low in compounds that can trigger inflammation. Therefore, the carnivore diet may help reduce chronic inflammation, potentially benefiting conditions such as arthritis, autoimmune diseases, skin conditions, and Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (CIRS).
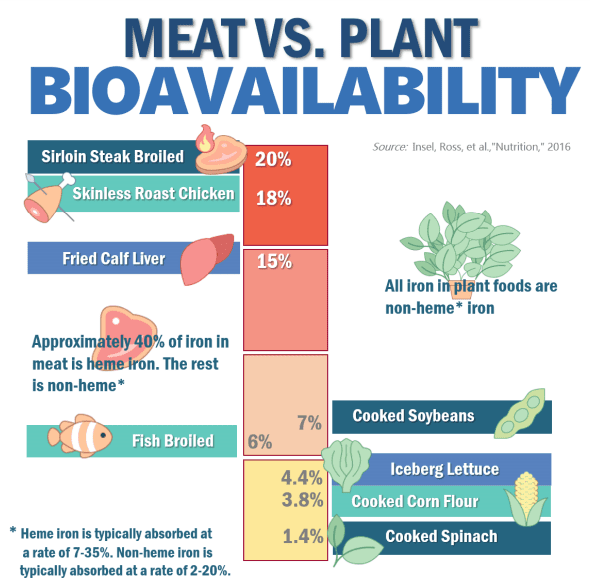

7. Increased Nutrient Intake: Meat and animal products are rich in essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. There are many nutrients that are required for optimal health that are either exclusively found in animal foods or aren’t very bioavailable from plant foods. The diet ensures a high intake of these nutrients, which are crucial for various bodily functions.
8. Elimination Diet Benefits: For those with food sensitivities or allergies, the carnivore diet acts as an elimination diet, helping to identify foods that cause adverse reactions. By starting with a very restricted diet and slowly reintroducing other foods, individuals can pinpoint which foods they should avoid.
9. Potential Improvement in Autoimmune Conditions: The carnivore diet may benefit those with autoimmune conditions by reducing the intake of potential trigger foods. This can lead to a decrease in symptoms for some individuals.
10. Hormonal Balance: The diet’s high fat and cholesterol content can positively impact hormone production, as these nutrients are vital for the synthesis of hormones such as testosterone and estrogen.
With only a handful of scientific studies published on the carnivore diet, our practice is currently working on creating peer-reviewed scientific papers to support all the therapeutic benefits we’ve witnessed from our own clinical practice of over 1000 meat-based patients.
The Importance of Enough Dietary Fat for Kids
Dietary fat is a crucial element in the diets of children, underpinning many aspects of their development and overall health. Fat is not just a source of energy; it plays several key roles in childhood growth and physiological processes.
Brain Development


Fats, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are essential for brain development. The human brain is about 60% fat, requiring these fatty acids for cognitive development, memory, and learning functions. This is especially critical in early childhood, a period marked by rapid brain growth.
Energy Source
Fat provides a concentrated source of energy, crucial for the high energy demands of growing and active children. It offers more than double the energy per gram compared to carbohydrates or proteins, supporting children’s active lifestyles and growth needs.
Nutrient Absorption
Dietary fats aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins – A, D, E, and K. These vitamins are integral for vision, bone growth, immune system functioning, and blood clotting. Insufficient fat intake can lead to poor absorption of these essential nutrients.
Cell Growth and Repair
Fats contribute significantly to the structure of cell membranes, facilitating growth and tissue repair. This function is particularly important for children, whose bodies are in a constant state of development.
Hormone Production
Fats are involved in hormone production, including those regulating metabolism, immune function, and growth. Proper hormonal balance is vital for normal growth and development during childhood.
Satiety and Taste
Fats enhance the taste and texture of food, making meals more palatable. They also contribute to a feeling of fullness, aiding in appetite regulation and maintaining a healthy weight.
Ensuring children consume adequate healthy fats is crucial for their development. This includes incorporating various fat sources such as fatty meats, dairy products, fatty fish, and other less-toxic plant-based sources into their diets. Adequate fat intake supports many physiological processes and is a cornerstone of healthy childhood development.
Not All Fats Are Created Equal
Understanding the nuances of dietary fats is crucial when it comes to feeding children, especially in distinguishing between healthy animal fats and other types of fats. Not all fats are created equal, and each type plays a different role in the body.
Monounsaturated Fats
Found abundantly in animal sources such as pork and in plant sources such as olives, these fats are known for their heart-healthy properties. In animal fats, monounsaturated fats come bundled with other nutrients such as vitamin E, which is less prevalent in plant-based monounsaturated fats. They are essential for cellular function and overall health.
Saturated Fats
These fats, predominant in animal products such as beef and dairy, are crucial for children’s development. They play a vital role in brain health, hormone production, and cellular integrity. Unlike trans fats, which are harmful and found in processed foods, naturally occurring saturated fats in animal products contribute positively to health, especially in the context of a low-carb diet.
Polyunsaturated Fats
These include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-3s are anti-inflammatory and found in fatty fish, omega-6s, which are more common in vegetable oils, can be pro-inflammatory in excess. Animal fats provide a more balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fats compared to many plant-based oils.
The key difference in animal fats lies in their composition and the additional nutrients they provide. Animal fats are not only sources of energy but also carry fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, which are essential for growth and development. In contrast, some plant-based fats, while beneficial, may lack these additional nutrients.
When considering fats in children’s diets, it’s important to focus on the quality and source of the fat. Healthy animal fats offer a unique combination of monounsaturated, saturated, and polyunsaturated fats, along with essential vitamins, making them an important part of a balanced diet for children.
The Bad Fats
Vegetable oils, seed oils, and hydrogenated vegetable oils, commonly categorized as “bad fats,” are increasingly scrutinized for their potential adverse health impacts, making them particularly unsuitable for children. Here’s why they should be avoided:
High Omega-6 Fatty Acids
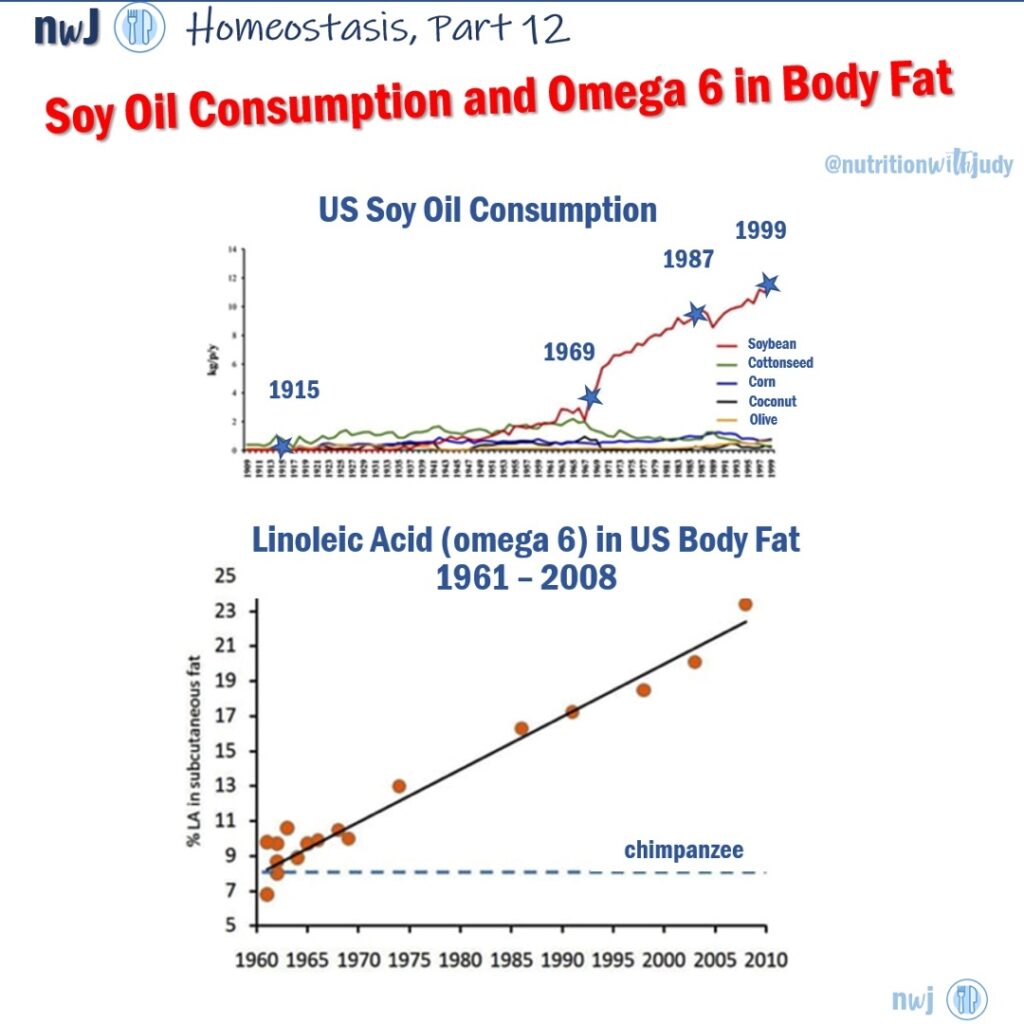
Vegetable and seed oils such as soybean, corn, and sunflower oil are high in omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6s are essential in moderation, excessive consumption can lead to an imbalance with omega-3 fatty acids, promoting inflammation. This imbalance is linked to chronic diseases, making these oils less desirable, especially for children whose bodies are still developing.
Trans Fats in Hydrogenated Oils
Hydrogenated vegetable oils are a primary source of trans fats, which are created during the hydrogenation process to solidify liquid vegetable oils. Trans fats are notorious for their detrimental effects on heart health and has been linked to other serious conditions such as breast cancer.They are strongly associated with an increased risk of heart disease and should be avoided entirely, especially in children’s diets.
Processing and Chemicals
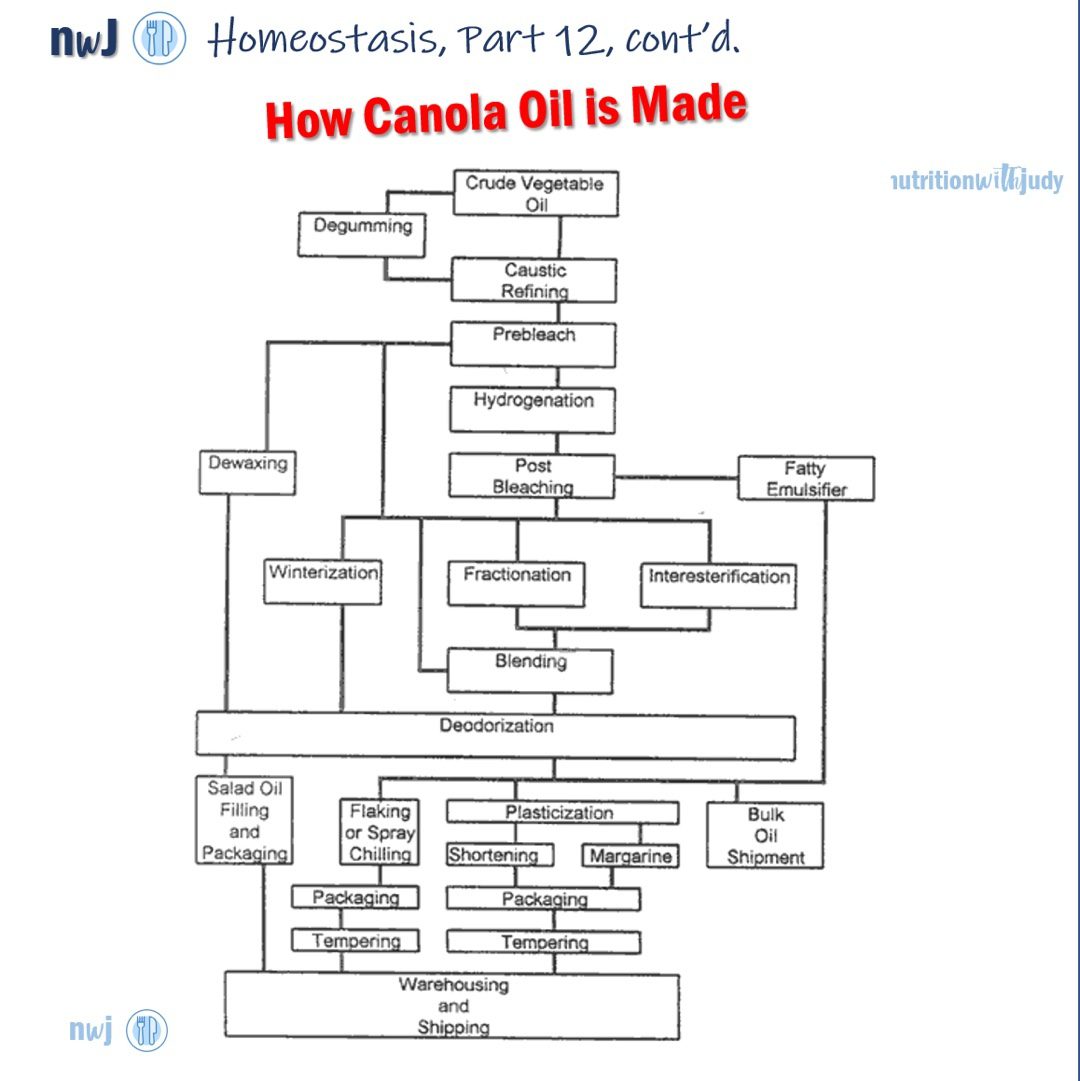

Many vegetable and seed oils undergo extensive processing, involving high temperatures and chemicals. This process can strip away beneficial nutrients and introduce harmful compounds. For instance, during high-heat processing, oils can oxidize, leading to the formation of harmful free radicals. Additionally, toxic solvents such as hexane are often used to extract these oils which are later on bleached and deodorized as these oils are often rancid from the complex processing requirements.
Impact on Cellular Health
The fatty acid composition of these oils can affect cellular membrane structure and function. Cells require healthy fats to maintain membrane integrity, and the predominance of unhealthy fats can compromise this, impacting various cellular functions and overall health.
Given these factors, it’s crucial for dietary guidelines, particularly for children, to emphasize the avoidance of these “bad fats.” Instead, focusing on healthier fat sources such as those found in whole foods with an emphasis on fatty meats.
Carbohydrates Are Not Essential


Carbohydrates, while a major part of many diets, are classified as a non-essential macronutrient. This means that unlike fats and proteins, which contain essential fatty acids and amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own, carbohydrates are not required to be obtained from the diet for survival and normal functioning.
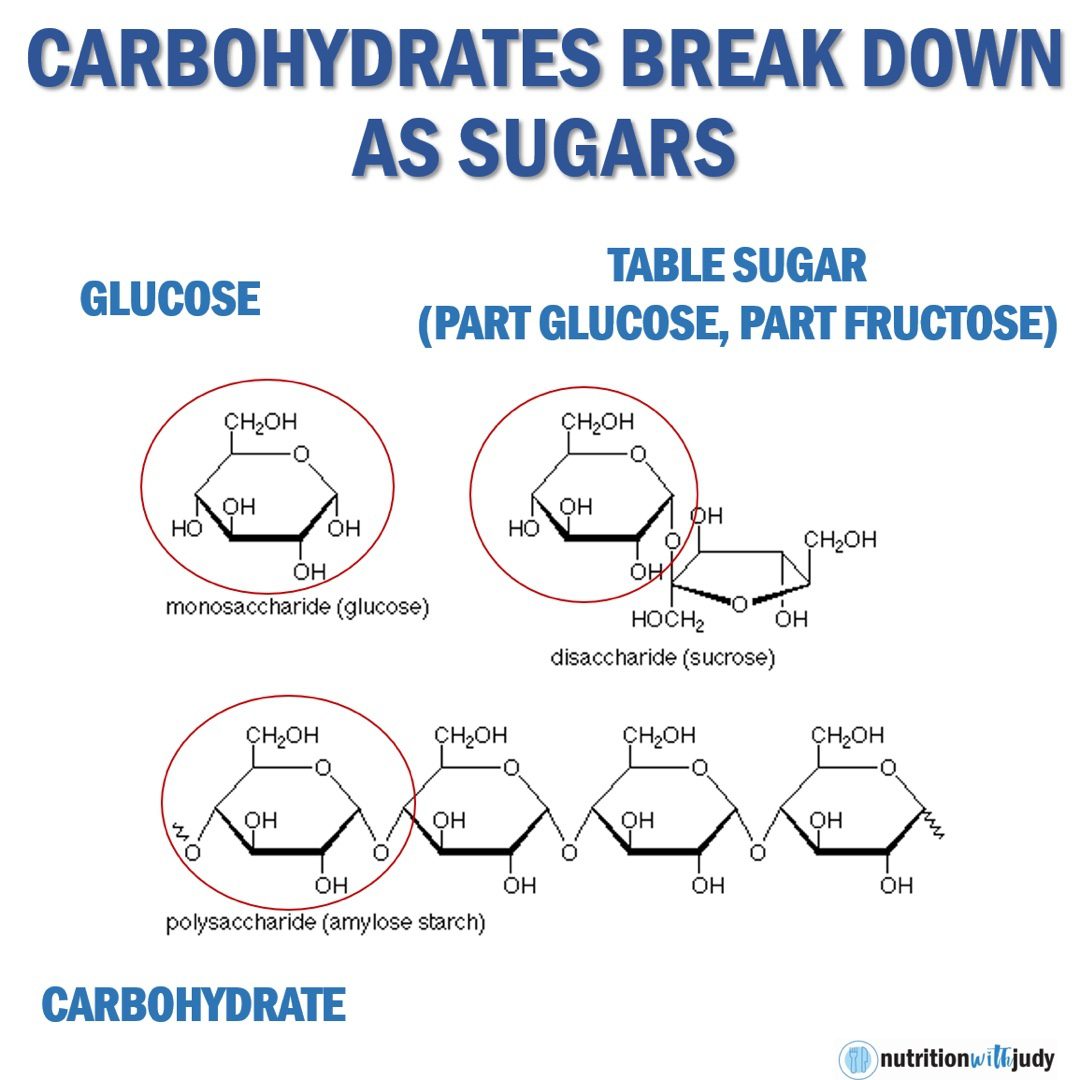

When carbohydrates are consumed, the body breaks them down into simpler sugars such as glucose, which is a primary energy source for cells. Glucose is especially important for the brain, which relies heavily on it for energy. However, the body has a remarkable ability to adapt to different dietary conditions.
In the absence of dietary carbohydrates, the body can produce the necessary glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis. This metabolic pathway synthesizes glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as lactate, glycerol, and the amino acids alanine and glutamine. These substrates can be derived from the breakdown of dietary proteins or from body tissues, such as muscle, in the absence of adequate dietary protein.
Gluconeogenesis ensures that the body maintains adequate blood glucose levels for the functioning of organs such as the brain and red blood cells, which rely on glucose as a primary energy source. This adaptive process highlights the body’s ability to sustain itself without dietary carbohydrates, reinforcing the idea that carbohydrates are a non-essential macronutrient.
While carbohydrates are a common energy source in many diets, they are not essential from a biological standpoint, as the body is capable of generating the glucose it needs through gluconeogenesis.
Why Limiting Carbs and Sugar Is Ideal for Children


Overconsumption of carbohydrates and sugar poses significant health risks for children, impacting their well-being both in the short and long term. Here’s a summary of the potential health issues associated with excessive carb and sugar intake:
- Obesity: High intake of sugary and high-carb foods can lead to excessive calorie consumption, contributing to weight gain and obesity in children. Obesity in childhood increases the risk of developing various health issues later in life, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excessive consumption of sugar and refined carbs can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. This condition, once rare in children, is becoming more common due to dietary habits. It can lead to lifelong health issues, including cardiovascular problems and nerve damage.
- Dental Problems: Sugary foods and drinks are a leading cause of dental cares (cavities) in children. The acid produced by bacteria feeding on sugar in the mouth erodes tooth enamel, leading to decay.
- Behavioral and Cognitive Impact: High sugar intake can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which may affect a child’s behavior and ability to concentrate. This can impact their academic performance and overall cognitive development.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet high in carbs and sugar often lacks essential nutrients, as these foods can displace more nutrient-dense options such as animal foods and safer vegetables and fruits. This can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals crucial for growth and development.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Long-term, a diet high in sugar and refined carbs can increase the risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease and fatty liver disease.
Moderating carbohydrate and sugar intake is crucial for children’s health. Encouraging a balanced diet with a focus on animal foods can mitigate these risks and promote healthier growth and development.
Children and Chronic Illness
The prevalence of chronic illnesses among children today is alarmingly high, with obesity and diabetes leading the charge. This disturbing trend can largely be attributed to lifestyle factors, especially dietary habits.
Obesity in children has become a global epidemic. The primary cause is an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calories expended, with a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats, and a sedentary lifestyle being major contributors. Childhood obesity is not just a cosmetic issue; it sets the stage for serious health problems, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Type 2 diabetes, once considered an adult condition, is now increasingly diagnosed in children. This shift is closely linked to the rise in childhood obesity. High consumption of sugary and processed foods leads to insulin resistance, the hallmark of type 2 diabetes. This condition can have long-term health consequences, including kidney, nerve, and eye damage.
The good news is that many of these conditions are preventable, and in some cases, reversible through diet and lifestyle changes. Adopting a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, reducing sugar and unhealthy fat intake, and increasing physical activity can significantly reduce the risk of these chronic diseases. It’s crucial to instill healthy eating habits in children from a young age, as this not only helps in preventing these conditions but also promotes overall health and well-being.
This scenario underscores the urgent need for dietary education and lifestyle changes among the younger population. By addressing these issues early on, we can pave the way for a healthier, disease-free future for our children.
Should Kids Eat the Carnivore Diet?
We generally recommend a keto or low-carb diet for children. While some days may include a more carnivore-diet-aligned eating plan, we believe that leveraging hormetic stress and building the immune system is important. Watch our YouTube video above for more information as to why we recommend this way of eating for kids. For more in-depth information regarding what you should be feeding your kids, we have a free Kids Nutrient Dense eBook and Low-Carb Lunch Ideas available here.
Educating Our Children for Healthy Relationships With Food
Educating children on developing a healthy relationship with food is paramount in nurturing their long-term well-being and health. This education is not about imposing strict dietary restrictions, but rather about teaching them the vital connection between their food choices and their physical and emotional health. A balanced approach, emphasizing the benefits of a meat-heavy, low-carb diet, can be instrumental in this learning process.
Understanding Food’s Impact on Health
Children need to comprehend how different foods affect their bodies and minds. A diet high in sugars and processed foods often leads to energy crashes, mood swings, and health issues such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Conversely, a diet rich in nutrients supports physical growth, cognitive development, and emotional stability.
Emphasis on Satiety and Nutritional Value
A meat-heavy, low-carb diet naturally leads to higher satiety due to the filling nature of proteins and fats. This approach helps children understand and listen to their hunger cues, preventing overeating. Protein-rich diets also supply essential nutrients for growth and development, making them a healthier choice compared to carb-laden diets.
Avoiding Sugar and Toxins
By focusing on a diet that limits sugar and unnecessary additives found in many processed foods, children learn to appreciate the taste and benefits of whole, unprocessed foods. This not only reduces their toxin exposure but also instills a preference for healthier food choices.
Portion Control Through Natural Satiety
A meat-heavy diet promotes natural portion control. Children eating nutrient-dense foods such as meat, eggs, and dairy are less likely to overeat as they feel fuller sooner and for longer periods. This natural regulation of food intake is a healthier and more sustainable approach compared to calorie counting or restrictive dieting.
Long-Term Health and Lifestyle Benefits
Instilling these values early on leads to healthier lifestyle choices in adulthood. Children who understand the importance of nutritious eating are more likely to maintain a balanced diet as they grow older, reducing their risk of chronic diseases.
Balanced Approach
While emphasizing the benefits of a meat-heavy, low-carb diet, it’s also important to teach children about the value of other food groups, including vegetables and fruits, in moderation. This helps in fostering a well-rounded dietary perspective, helping reduce the risk of binging once your children become adults.
Overly limiting and restricting food choices can also cause a negative relationship with food, making it critical to have a balanced approach. Incorporating healthier alternatives while educating children on the health impact of these food decisions can help your kids embrace food freedom and potentially better learn moderation from a younger age.
Educating children about the importance of making informed food choices and the benefits of a meat-heavy, low-carb diet can profoundly impact their immediate and future health. This education should focus on balance and understanding, rather than restriction, to promote a healthy, lifelong relationship with food.
Closing Thoughts On the Carnivore Diet for Children
In exploring the carnivore diet for children, we’ve delved into various aspects, highlighting its potential benefits while recognizing the need for a balanced approach. While a strict carnivore diet is rare and typically not recommended for children, there are exceptions in cases of chronic illnesses. For some children with specific health conditions, a strictly carnivorous diet might be beneficial as a temporary therapeutic intervention, under medical supervision, to manage symptoms or identify food sensitivities.
However, for the majority of children, a meat-heavy, low-carb diet strikes a healthier balance. This diet, rich in high-quality animal proteins and fats, supports essential aspects of childhood development, including brain growth, hormonal balance, and overall physical development. Animal fats, particularly, play a crucial role in cognitive development and energy provision. Additionally, this diet model emphasizes the importance of satiety and nutrient density, teaching children to respond to their body’s natural hunger cues, thereby avoiding overeating and excessive sugar intake.
Importantly, this approach is not about severe restriction but rather about making informed food choices that impact health and well-being. It’s about educating children on the importance of diet in their overall health, understanding the impacts of different foods, and fostering a healthy relationship with food. Emphasizing a diet rich in meats and low in carbohydrates, while not overly restrictive, can help children thrive and develop optimally.
Work With Our Trusted Carnivore Diet Functional Nutritional Therapy Practitioners
The Nutrition with Judy practice is honored to be a trusted carnivore diet practitioner support serving clients from around the globe. We’re passionate about helping our clients achieve root-cause healing in order to lead the best quality of life possible that’s nearly symptom-free. Our team is dedicated to educating our community about the incredible benefits of the carnivore diet. We welcome you to explore our free resources and are always available to support you through personalized protocols. Our Symptom Burden Assessment (SBA) is the perfect starting point for discovering your root cause and is required to work with our team— you can learn more in-depth about this powerful tool here.
Start your root-cause healing journey today and contact us any time with any questions or concerns.
DISCLAIMER: This content is for educational purposes only. While we are board-certified in holistic nutrition and are nutritional therapy practitioners, we are not providing medical advice. Whenever you start a new diet or protocol, always consult with your trusted practitioner first.