
The Importance of DHA for Brain Health


Similar to all processes within the body, brain health begins with proper nutrition. Standard care and mainstream nutrition often tout plant “superfoods” for boosting cognitive function and memory. It’s common to hear about miracle flavonoids from blueberries, vitamin-rich leafy greens, omega fatty acids and safer protein options from nuts, antioxidants from turmeric, and more as important staples for brain food.
While a plant-based diet has been coveted for its supposed brain health benefits, the reality is that there are certain nutrients that you simply cannot get from plants. These essential nutrients that are only found in animal foods are foundational for various physiological functions including brain health. One of these nutrients that’s required for proper brain health and overall wellness is docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Let’s take a closer look at what DHA is, the importance of DHA and brain health, and what the best sources of this brain food are.
What Is DHA?
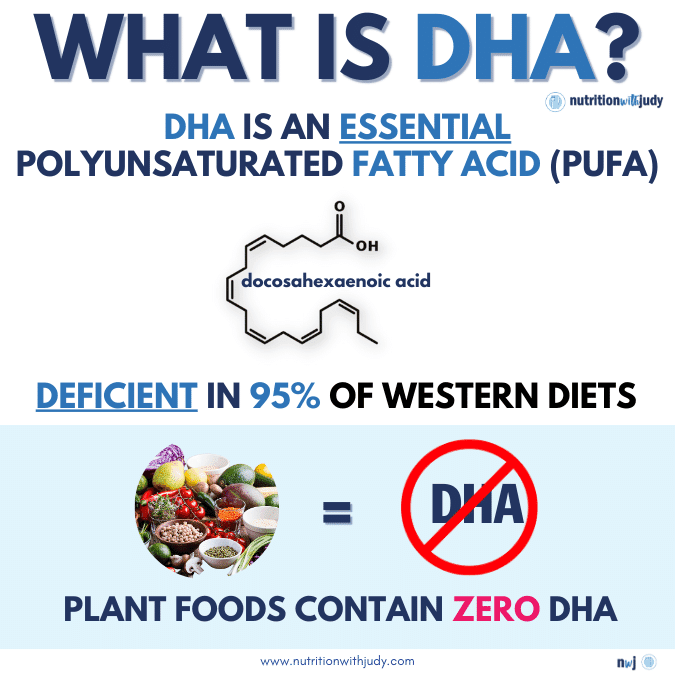

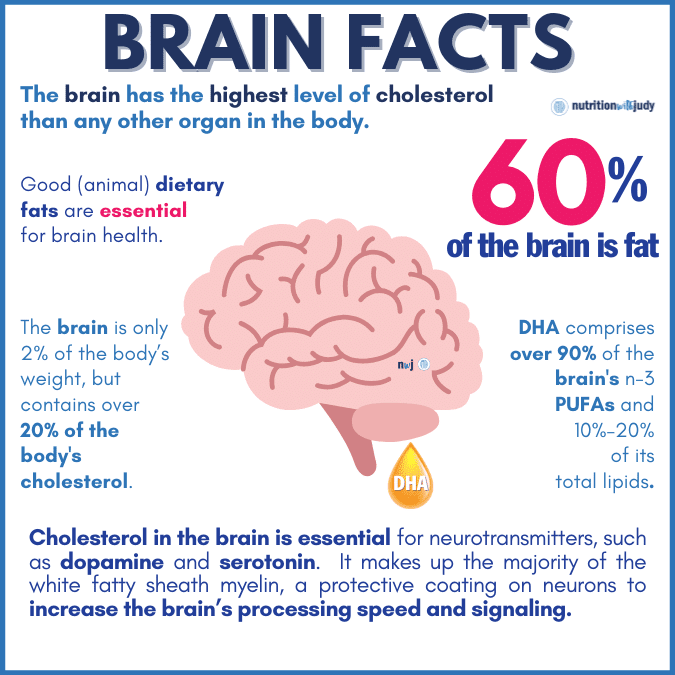
DHA is a type of omega-3 fatty acid that’s the primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, eyes, and skin. DHA also comprises over 90% of the omega-3 fatty acids in your brain and constitutes up to 25% of its total fat content.
It is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that’s predominantly available from animal sources. The body can’t produce the amount of omega-3s required to survive— omega-3s are essential nutrients that you must obtain from food.
There are two main types of omega-3 fatty acids: long-chain and short-chain. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids are DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Short-chain omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
DHA and EPA are both abundantly found in fatty fish and shellfish such as salmon, sardines, oysters, and caviar. Small amounts of DHA also occur naturally in meat, eggs, and dairy from pasture-raised, grass-finished animals. Meat that is grain-fed has a much lower amount of omega-3s. DHA is also found in human breastmilk and algae— algae is classified as a protist and not a plant. There are no plant sources for DHA, we’ll expand on this nuance further in the article.
The Role of DHA in the Body
DHA is vital for every cell in the body. It is mainly located within cell membranes, making the gaps and membranes between the cells more fluid. This in turn makes it easier for cells to send and receive electrical signals. Having adequate levels of DHA is believed to enhance the efficiency and speed of communication between nerve cells. Therefore, having low levels of DHA in your eyes or brain can result in slower cell signaling, causing poor eyesight or impacted cognitive function.
DHA and Brain Health
DHA is the main type of omega-3 that comprises the brain and is essential for all nervous system functions. It is critical for cognitive function— individuals consuming a diet low in omega-3s often experience cognitive benefits from dietary or supplementary DHA.
DHA also contributes to improved memory function. Studies show that individuals with Alzheimer’s disease have lower levels of DHA in their brains. One review reported that a higher intake of omega-3s was linked to a reduced risk of mental decline, an important characteristic in different types of dementia. Research shows that DHA may act more as a preventative for cognitive decline and disorders if you start increasing your levels early.
Additionally, DHA plays the following roles in brain health:
- Critical for cortex development– the part of the brain responsible for higher thinking
- Required for brain function maintenance
- Modulates neuroinflammation
- Regulates pain
- Alleviates oxidative stress
- Essential for the growth and development of infant brains
- Maintains the blood-brain barrier
- Modulates cellular signaling
- Buffers electron flow at the synapses
The Health Benefits of DHA
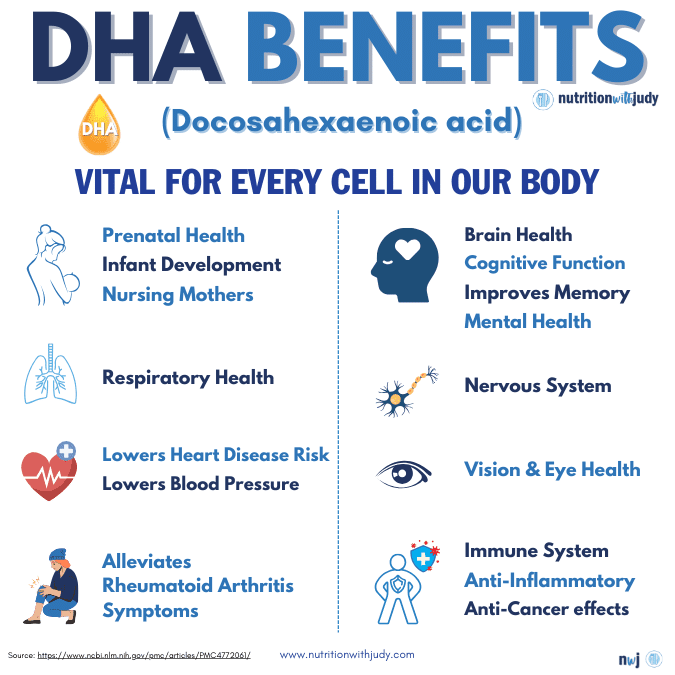

Since DHA plays a critical role for every cell within the body, it offers a wide scope of health benefits in addition to brain health, including:
- Prenatal health and infant development: Since DHA accumulates in the fetal brain during pregnancy, it is believed to support neurodevelopment. Animal studies have shown a lack of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy is linked to visual and behavioral deficits not reversible with postnatal supplementation. Adequate DHA throughout pregnancy is required for proper infant development. An analysis of two studies reported that women consuming 600-800mg of DHA daily during pregnancy had a reduced risk of early preterm birth by more than 40% in the US and 64% in Australia.
- Cardiovascular benefits: DHA and other omega-3s can help lower triglyceride levels— too many triglycerides can increase your risk for atherosclerosis. One study found that supplementing with high doses of DHA increased the omega-3 index which is a blood marker linked to the reduced risk of sudden heart-related death. It can also lower blood pressure, helping reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Respiratory health: Higher levels of omega-3s have been linked to improved lung health. One animal study reported that a diet high in DHA reduced the lung’s inflammatory response to acute dust exposure. While research is still ongoing, DHA and EPA show therapeutic promise for their anti-inflammatory effects on the lungs, reduced rate of lung function decline, and certain lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Joint support: Since DHA is more effective at reducing inflammation than EPA, it can offer relief for individuals with arthritic conditions. A recent study discovered that omega-3s may modulate the autoimmune inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Vision and eye health: Research supports that DHA may help preserve your vision. One study discovered that DHA prevented age-related vision loss in mice. Omega-3s are also being researched for their therapeutic potential for eye conditions— a randomized controlled trial reported that omega-3s improved dry eye syndrome. Another randomized controlled trial found that omega-3 supplementation reduced intraocular pressure among adults.
- Immune system boost: Omega-3s have been found to rebalance immune function during the pre-autoimmunity stage. DHA metabolites balance immune system modulators such as B-cells, cytokines, and lymphocytes. Since omega-3s are vital for immune system functioning, researchers are also looking into their therapeutic potential for supporting healthy inflammation and immunity. One study showed that DHA and EPA-rich fish oils enhance the function of B-cells which are a type of white blood cell that fights pathogens. Dietary omega-3s enhance cell function, including your immune cells.
Additionally, research shows that DHA may improve ADHD; support muscle recovery after workouts; support men’s reproductive health; protect mental health, particularly with depression; and reduce the risk of certain cancers.
Deficiencies in DHA are associated with:
- Fetal alcohol syndrome
- ADHD
- Cystic fibrosis
- Phenylketonuria
- Psychiatric and mood disorders
- Aggression
The Best Sources for DHA
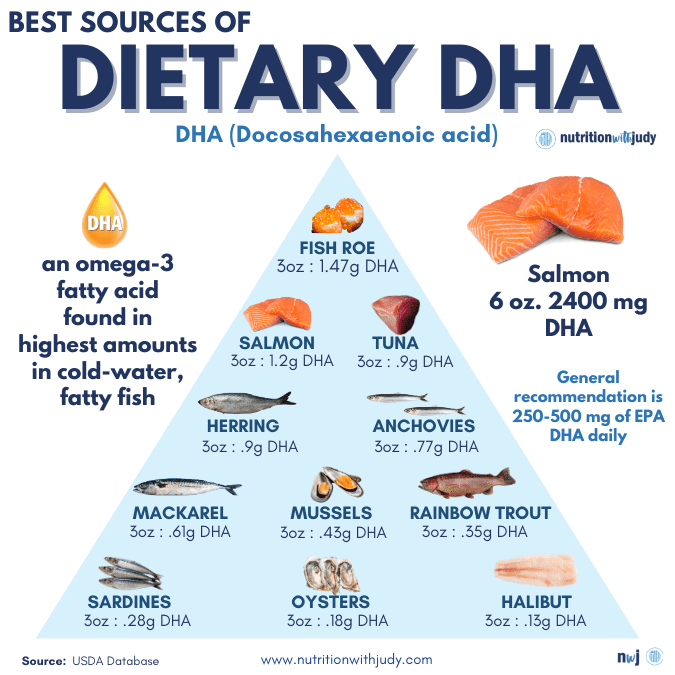

As mentioned above, DHA is abundantly found in fatty fish and shellfish such as salmon, sardines, oysters, and caviar. Small amounts of DHA also occur naturally in meat, eggs, and dairy from pasture-raised, grass-finished animals.
Algae can also be a good source of DHA. When you compare algae oil with fish oil supplements, you’ll notice that algae oil typically has lower amounts of EPA and DHA per serving. Fish oil typically contains both DHA and EPA in varying ratios which may be advantageous for certain health outcomes— some algae oils may only contain DHA, though there are products with both.
The bioavailability of DHA and EPA from fish oil is generally high. For algae oil, the bioavailability can also be good but it may depend on the specific form of algae and processing methods used. While algae oil is not typically associated with anti-nutrients, some forms of algae contain substances that can interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients. This is generally more of a concern with whole algae consumption rather than purified algae oil.
However, algae can be an alternative source of DHA for those who can’t eat fish due to shellfish allergy. For those with histamine intolerance who are unable to tolerate fish oil supplements or grocery-store fish, Vital Choice offers low-histamine wild-caught king salmon options if you prefer consuming fish over algae.
Overall, seafood offers the best bioavailable source for DHA.
DHA vs. ALA
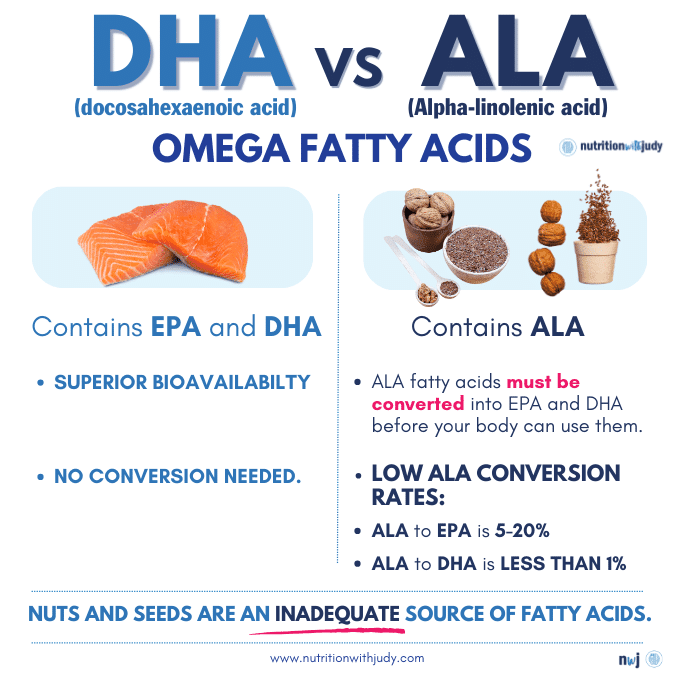
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is a short-chain omega-3 fatty acid that’s found in plants. While it may offer some health benefits, it is significantly less potent than DHA and EPA. The important nuance here is how the body utilizes ALA. Plant foods are not a good source of complete omega-3s since our bodies need DHA and the body doesn’t convert ALA to DHA efficiently. ALA fatty acids must be converted into DHA and EPA before the body can utilize them.
The ALA to EPA conversion rate is between 5% to 20% while the ALA to DHA conversion rate is less than 1%. That means that plant foods such as nuts and seeds are not an adequate source of fatty acids.
How Much DHA Do I Need?
There currently is no official set recommended daily allowance (RDA) for DHA or EPA. Health organizations all have different recommendations around how much DHA is required daily for optimal wellness. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends one to two servings of seafood weekly to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and approximately one gram of DHA plus EPA, preferably from fish oil, for those with existing coronary disease.
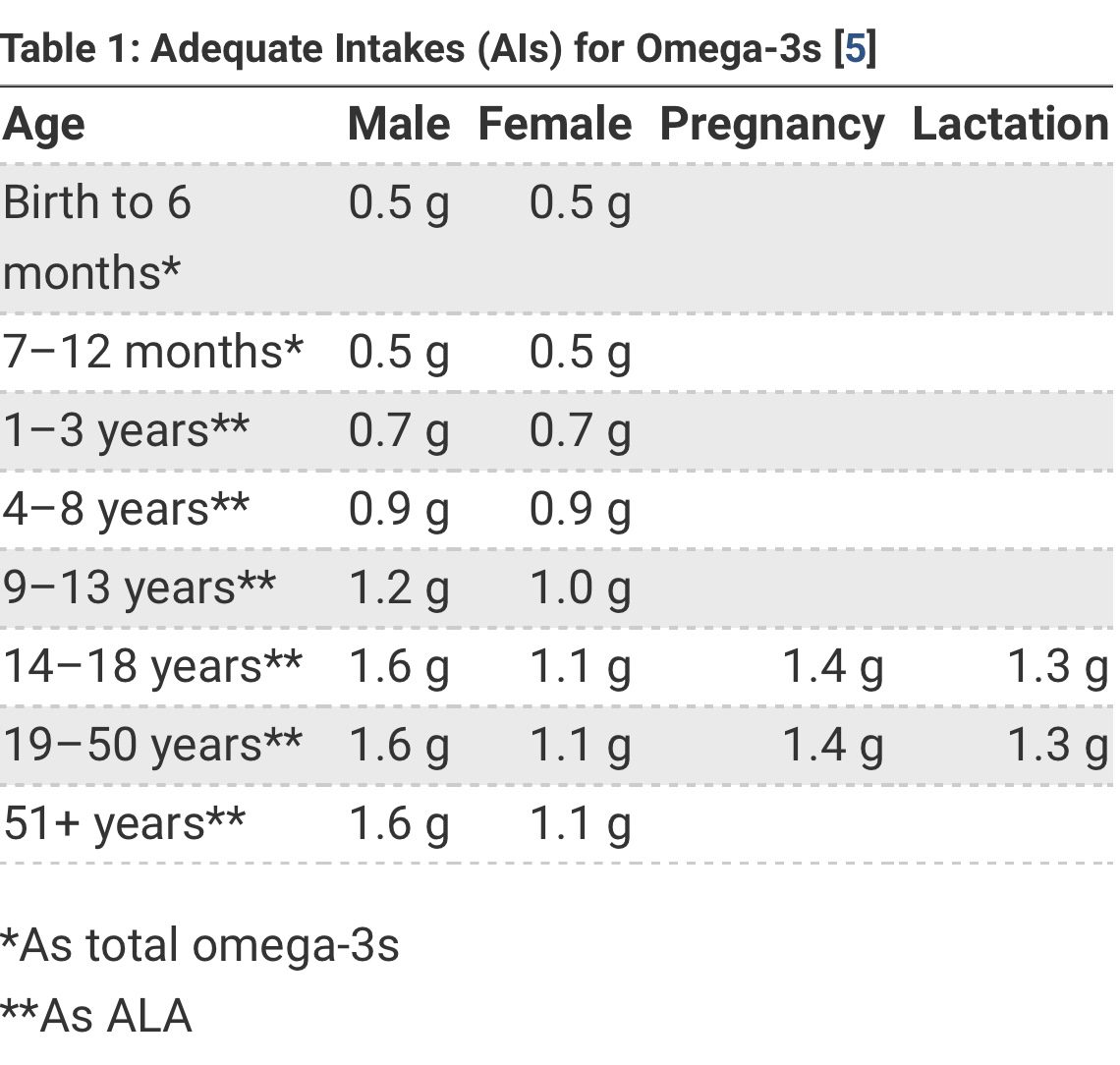
The daily omega-3 recommendation combines both DHA and EPA for the following age groups:
These recommendations are the minimum amount of omega-3s you should be eating daily. Remember the nuance around ALA— use the recommendations in the graph but apply them to DHA and EPA rather than ALA. Higher doses can be warranted for certain conditions. However, the following are symptoms of taking too much omega-3s. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, talk to your trusted practitioner and consider reducing your omega-3 intake.
- High blood sugar: High amounts of omega-3s may increase blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes
- Bleeding gums and nosebleeds: Two hallmark signs of excess fish oil supplementation
- Low blood pressure: Fish oil’s ability to reduce blood pressure is well-documented
- Diarrhea: One of the most common side effects particularly with taking high-dose fish oils
- Vitamin A toxicity: Certain types of omega-3 supplements such as cod liver oil are high in vitamin A which can lead to vitamin A toxicity
- Insomnia: High-dose fish oils may worsen symptoms of insomnia and anxiety for individuals with a history of depression
Closing Thoughts


If DHA is so essential for everything from brain health to cellular function, why are women told to stay away from sushi while pregnant or nursing? If women have access to high-quality sushi, we question this advice. Is it better to get DHA and EPA in a formula and supplements than from these natural powerhouse foods? We don’t think so.
Standard care advises pregnant women to stay away from raw fish because of possible heavy metals, bacteria, and other toxins. Yet pregnant women are also recommended to get multiple vaccines that contain toxins during their pregnancy. If you are still concerned with mercury poisoning from fish during pregnancy, make sure you’re supplementing with high-quality fish oils or algae.
DHA is one of many nutrients that aren’t available in the plant kingdom. The repercussions of DHA deficiency are profound and can’t be reversed with postnatal supplementation. Whatever life stage you’re in, make sure you’re getting plenty of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids such as DHA and EPA in your diet.
Work With Our Trusted Carnivore Diet Functional Nutritional Therapy Practitioners
The Nutrition with Judy practice is honored to be a trusted carnivore diet practitioner support serving clients from around the globe. We’re passionate about helping our clients achieve root-cause healing in order to lead the best quality of life possible that’s nearly symptom-free. Our team is dedicated to educating our community about the incredible benefits of the carnivore diet. We welcome you to explore our free resources and are always available to support you through personalized protocols. Our Symptom Burden Assessment (SBA) is the perfect starting point for discovering your root cause and is required to work with our team— you can learn more in-depth about this powerful tool here.
Start your root-cause healing journey today and contact us any time with any questions or concerns.
DISCLAIMER: This content is for educational purposes only. While we are board-certified in holistic nutrition and are nutritional therapy practitioners, we are not providing medical advice. Whenever you start a new diet or protocol, always consult with your trusted practitioner first.








Lorraine Hanson
January 30, 2024 at 11:59 amJudy,
Thank you so much for this article
I have white matter disease that they say is advancing. I am doing everything in my power to stay on top of this but I am having muscular issues and I notice some cognitive issues (especially when tired).
How would I best obtain DHA since I am not a fan of salmon?