Should Bull Testicles Be In My Carnivore Diet?


The carnivore diet, a nutritional approach that centers around animal-based foods, often stirs debate around the inclusion of organ meats such as bull testicles. Certain wellness influencers in the carnivore community advocate for the consumption of organ meats due to their rich nutrient profile, which includes essential vitamins and minerals that may be limited in muscle meats. This advocacy is based on the belief that such organs can provide unique health benefits, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of the diet.
However, the role of organ meats in the carnivore diet is nuanced. It’s essential to understand that while some individuals may experience health improvements by incorporating these nutrient-dense foods, many others have achieved remarkable healing and wellness benefits on a carnivore diet without them. This variance underscores the importance of individualized nutrition. At our holistic wellness practice, we emphasize the need to tailor dietary choices to each person’s unique health needs and goals. We recognize that dietary success and health optimization are highly personal, and what works well for one individual may not be as effective for another.
Our approach is rooted in the understanding that the human body’s nutritional requirements can vary greatly, influenced by factors such as genetic makeup, lifestyle, and existing health conditions. We encourage our clients to listen to their bodies and adjust their diets accordingly, whether that includes organ meats like bull testicles or not. The key is to find a balance that supports individual health objectives while ensuring overall well-being.
So, let’s take a closer look at the what bull testicles have to offer and if they should be included in your carnivore diet.
What Is the Carnivore Diet?

The carnivore diet is a nutritional approach centered around consuming primarily animal-based foods, often seen as a potent tool for addressing a variety of health issues, including diabetes, mental health conditions, and metabolic diseases. This diet focuses on the consumption of meat, emphasizing its nutrient density and bioavailability. However, within the carnivore diet community, several variations cater to different health needs and preferences:
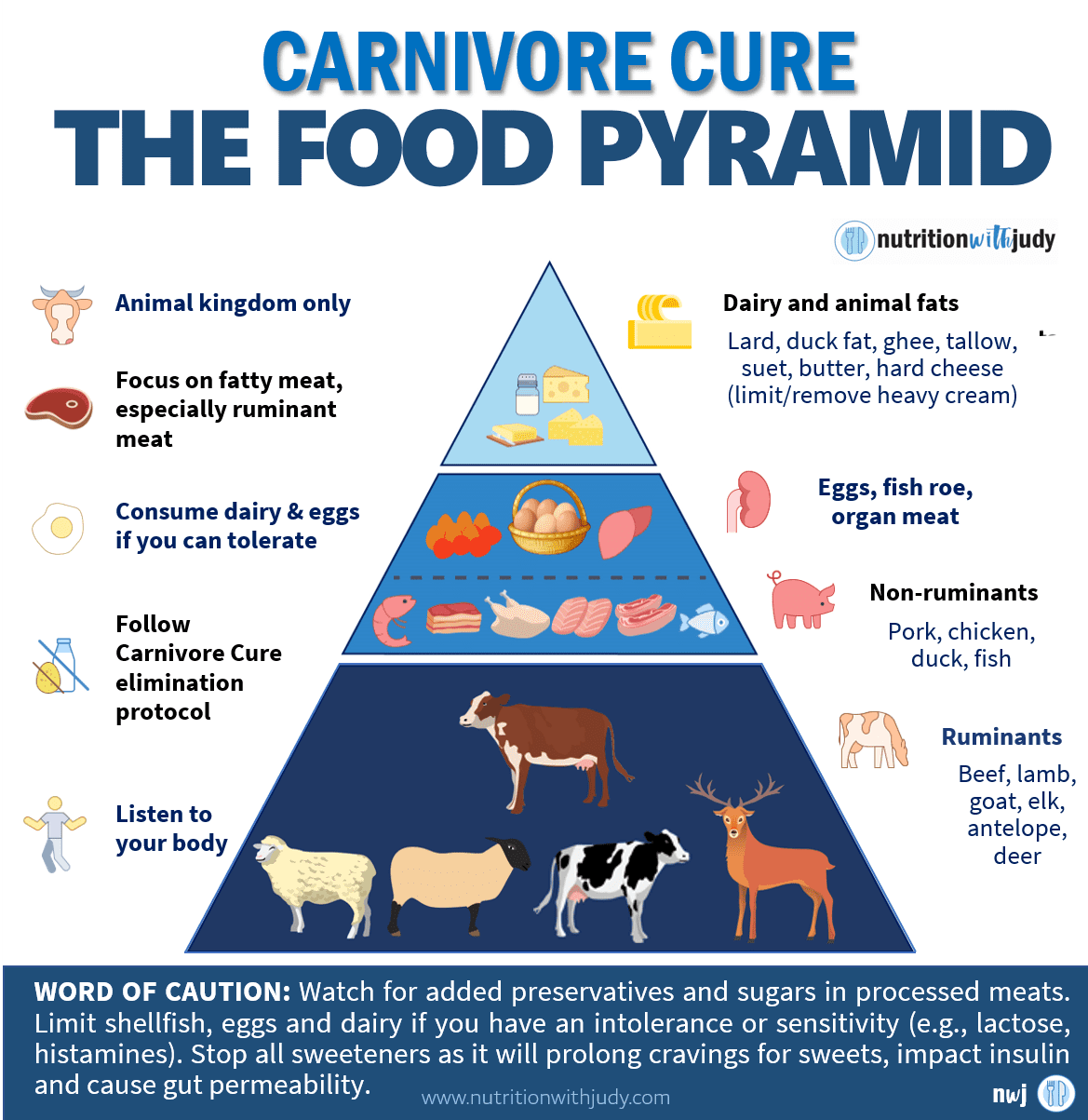
- Beef-Only Carnivore Diet: This strict version limits consumption to only beef, water, and sometimes salt. It’s favored for its simplicity and is ideal as an elimination diet as well as for supporting deeper health concerns.
- Lion Diet: A highly restrictive form, it focuses exclusively on ruminant meats (such as lamb, goat, bison, and beef), salt, and water. This variation is often used for elimination purposes to identify food sensitivities as well as support deeper health issues.
- Nose-to-Tail Carnivore Diet: Encourages consuming all parts of the animal, including organ meats, to maximize nutrient intake. This approach aims for a more balanced nutrient profile by including a variety of animal product. However, there’s a lot of nuance when it comes to eating organ meats. Always work with your trusted carnivore diet practitioner to explore if organs should be in your diet.
- Zero-Carb Carnivore Diet: While all carnivore diets are low in carbs, this version includes minimal carbs from dairy and eggs. The addition of these animal products provides better variety in nutrients and is ideal for those who tolerate dairy and eggs.
- Carnivore Keto Diet: Combines principles of the ketogenic diet with the carnivore diet, emphasizing high fat and moderate protein intake while maintaining very low carbs. Lower toxicity plant options are included such as avocados and pickles.
- Carnivore-ish Keto Diet: A less strict version, allowing for minimal plant intake while maintaining a focus on high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carb principles. With more keto options including sweetener alternatives and certain nut products, this can be a great option for those who have healed, are metabolically healthy, and don’t have food addiction concerns.
- Animal-Based Diet: A different approach that includes organs, raw dairy, honey, and fruit. In our clinical practice, we generally see individuals who are very athletic, metabolically flexible, and free of sugar addiction do well on this type of diet. Similar to the Ray Peat diet, we don’t usually recommend this variation.
Each variation of the carnivore diet offers different benefits and challenges, making it crucial for individuals to consider their unique health situations and goals when choosing the most suitable approach.
What Are the Benefits of the Carnivore Diet?
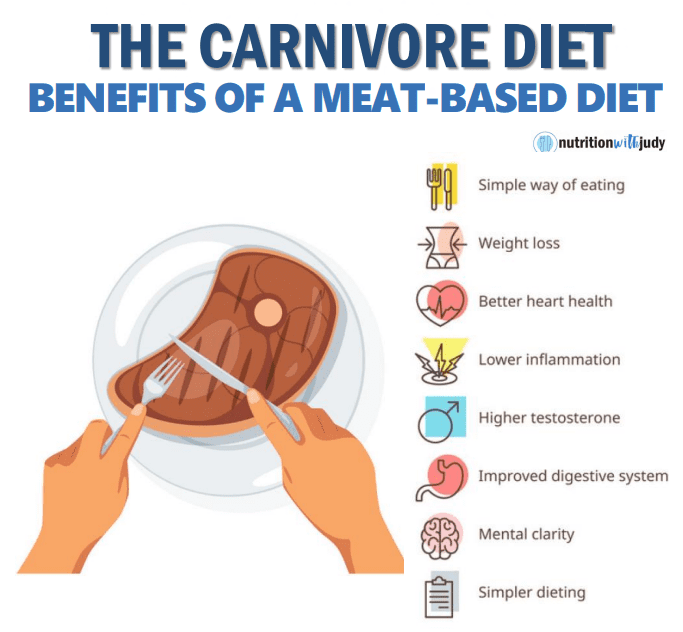

The carnivore diet, characterized by its exclusive focus on animal-based foods, has garnered significant attention for its numerous health benefits. This diet is not just a dietary choice but a potential solution for various health issues. Below is a summary of the key benefits of the carnivore diet, as evidenced by personal experiences and nutritional insights:
- Mental Health Improvement: Many individuals have reported significant improvements in mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety, after adopting the carnivore diet. This diet has been described as life-saving for some, freeing them from long-term reliance on antidepressants and helping them overcome love-hate relationships with food.
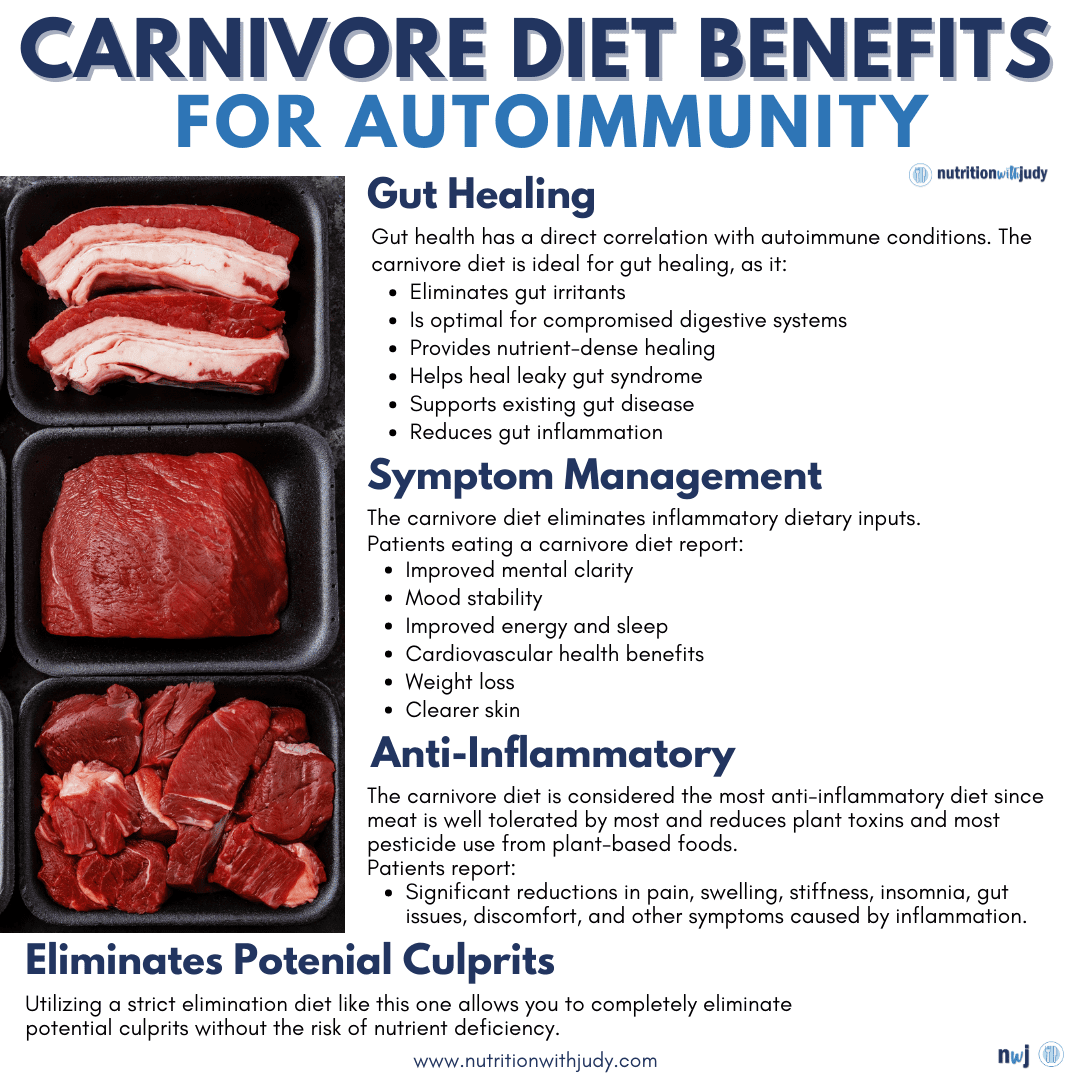

- Autoimmune and Chronic Illness Relief: The carnivore diet has shown promise in alleviating symptoms of autoimmune diseases and other chronic illnesses. For example, individuals have reported enhanced mobility and reduced symptoms of autoimmune conditions when following a ketogenic carnivore diet. This suggests the diet’s potential in managing chronic health issues.
- Identification of Food Sensitivities: The carnivore diet acts as an effective elimination diet, helping individuals identify food sensitivities. Since many food sensitivity tests are unreliable, the carnivore diet offers a practical approach to understanding how different foods affect one’s body.
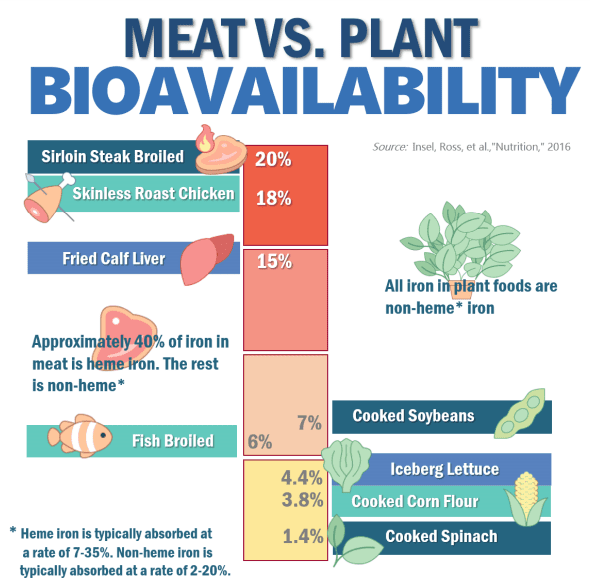

- Nutritional Benefits: Despite concerns about potential nutritional deficiencies, the carnivore diet is rich in several essential nutrients. It can be particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance, gut issues, mineral imbalances, and mental health imbalances. By focusing on meat, the diet provides a high-fat, nutrient-rich eating plan that addresses undernutrition issues prevalent in modern diets.
- Diverse Nutritional Sources: While the carnivore diet primarily revolves around meat consumption, it doesn’t restrict the variety of animal-based foods. Including different meats such as salmon, pork, and shellfish can offer a balanced intake of omega-3s, thiamine, copper, and zinc. This diversity is crucial for addressing specific health concerns and ensuring a well-rounded nutrient profile.
- Weight Management and Metabolic Health: The diet’s high protein and fat content can aid in weight management and improve metabolic health. Its effectiveness in addressing type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and other metabolic diseases has been noted, making it a viable option for those looking to manage these conditions.


- Digestive Health: Many people find relief from digestive issues on the carnivore diet, as it minimizes intake of foods that can irritate the gut, such as grains, legumes, and sugars.
- Simplicity and Satiety: The diet’s simplicity, focusing on meat and animal products, eliminates the need for complex meal planning. It also provides high satiety, which can reduce overall calorie intake and prevent overeating.
The carnivore diet offers a range of benefits, from mental health improvements to relief from chronic illnesses, and from identifying food sensitivities to providing a nutrient-rich eating plan. Its adaptability to include a variety of animal-based foods ensures that individuals can tailor the diet to their specific health needs and preferences. However, it’s essential to note that individual experiences with the diet can vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. As always, it’s advisable to consult with your trusted healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.
Customizing the Carnivore Diet for Individual Needs
The carnivore diet’s flexibility allows for customization to suit individual dietary requirements:
- Incorporating a Variety of Meats: Beyond just beef, including different meats such as salmon for omega-3s, pork for thiamine, and shellfish for copper and zinc can help balance nutritional intake. This variety ensures a broader range of nutrients, catering to specific health requirements.
- Adjusting Fat-to-Protein Ratios: Depending on individual health goals and conditions, the ratio of fat to protein can be adjusted. For instance, those focusing on weight loss might opt for a higher protein approach, while others looking for hormonal balance might increase fat intake.
- Addressing Nutritional Excesses: It’s crucial to avoid nutritional excesses, as they can lead to imbalances and health issues. The carnivore diet can be adjusted to prevent an overload of certain nutrients, which is essential for individuals with specific health conditions such as heavy metal toxicity or liver issues.
- Experimentation and Adaptation: The key to success with the carnivore diet is experimentation and adaptation. What works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust your diet accordingly, whether it means focusing on certain types of meats or modifying the fat and protein content.
The carnivore diet can be a powerful tool for improving health, but it’s not a universal solution. Its success depends on customization to individual needs and health goals. By adjusting the types of meats consumed, the macronutrient ratios, and being mindful of nutritional balance, the carnivore diet can be tailored to benefit a wide range of individuals.
What Are Bull Testicles?
Bull testicles, commonly known as “Rocky Mountain oysters,” “prairie oysters,” or “calf fries,” are a unique culinary delicacy. Originating from the practice of castrating young male cattle to promote growth, these testicles have been repurposed into a food item, especially popular in certain regions of the United States and Canada. They are considered a novelty dish in some cultures and are often associated with ranching and cowboy cuisine.
In terms of preparation, bull testicles are usually peeled to remove the tough outer membrane, then sliced or flattened. The most traditional and popular method of cooking is deep frying. Before frying, they are often coated in a seasoned batter or bread crumbs, similar to the preparation of fried chicken or other breaded meats. This process gives them a crispy exterior while keeping the inside tender. They can also be grilled, sautéed, or broiled, depending on personal preference or regional variations.
As for consumption, bull testicles are often served as an appetizer or a main course, accompanied by various dipping sauces, such as cocktail sauce, hot sauce, or a simple mixture of ketchup and mayonnaise. In some establishments, they are served alongside side dishes like fries, coleslaw, or vegetables. In the carnivore community, certain influencers promote eating bull testicles raw. Others will grill or fry the testicles with the addition of salt.
The taste of bull testicles is often described as mild and meaty, somewhat akin to venison or a very tender cut of beef. They are praised for their unique texture and flavor, which can be enhanced by the seasoning and method of cooking. In addition to being a culinary curiosity, they are also a source of protein and other nutrients.
While they might not be to everyone’s taste, bull testicles are a novel and interesting aspect of certain food cultures, offering a different perspective on the use of animal products in cuisine. For adventurous eaters or those interested in regional delicacies, trying bull testicles can be an intriguing and surprisingly enjoyable experience.
Do Bull Testicles Contain Any Nutrients?
Bull testicles are a unique and nutritious food source. They are packed with various essential nutrients, each contributing to different health benefits:
Protein
Bull testicles are a good source of high-quality protein, which is crucial for muscle repair, growth, and overall bodily function. Protein is also essential for maintaining and building muscle mass, making it particularly beneficial for athletes and those looking to improve their physical fitness.
Vitamins
They are rich in various vitamins, including B vitamins such as B12, which are vital for nerve function and the production of DNA and red blood cells. They also contain other B vitamins such as thiamine and riboflavin, essential for energy metabolism and overall health.
Minerals
Bull testicles provide essential minerals such as zinc, which is crucial for immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. They are also a source of selenium, an antioxidant that plays a key role in thyroid hormone metabolism and reproduction.
Fatty Acids
They contain healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. These fats can help lower the risk of heart disease, reduce inflammation, and support brain health.
Cholesterol
Dietary cholesterol, such as that found in bull testicles, plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Contrary to previous misconceptions, cholesterol is essential for the body. It is particularly important for hormone production and brain function. For instance, cholesterol is a fundamental building block for various hormones, including testosterone, which is vital for maintaining energy, muscle mass, and overall well-being.
Additionally, 25% of the body’s cholesterol is located in the brain, which is composed of about 60% fat. This cholesterol is critical for brain health, supporting cognitive functions and neural integrity.
Hormones and Other Bioactive Compounds
Bull testicles may contain hormones and other bioactive compounds that could potentially have various health effects, though more research is needed in this area.
Bull testicles are a nutrient-dense food that offers a variety of health benefits due to their rich content of proteins, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. They can be a valuable addition to the diet, especially for those looking to increase their intake of high-quality animal proteins and essential nutrients. However, as with any food, they should be consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet.
Do Bull Testicles Contain Bioavailable Testosterone?
There is a common misconception that consuming bull testicles, or any animal testicles, can significantly boost testosterone levels in humans. However, the bioavailability of testosterone from ingesting bull testicles is minimal, if at all present. Testosterone, similar to other hormones, is largely broken down in the digestive process and does not directly contribute to the hormonal balance in the human body when consumed in food form.
The idea of eating bull testicles to increase testosterone levels is more folklore than science. Testosterone in foods does not directly translate into increased testosterone levels in the body. The human endocrine system is complex and regulated by numerous factors, including but not limited to dietary intake. The body synthesizes most of its testosterone endogenously, and dietary sources are not a primary contributor.
Regarding the quantity one would need to consume to match testosterone replacement therapies, it’s impractical and ineffective to rely on bull testicles for this purpose. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) typically involves medically supervised administration of testosterone through injections, patches, or gels to achieve physiological levels. This is a controlled process, carefully monitored by healthcare professionals, to address specific medical conditions like hypogonadism.
While bull testicles are a nutritious food rich in proteins and various micronutrients, they are not a practical or effective source of bioavailable testosterone for therapeutic purposes. Relying on them as a substitute for testosterone replacement therapy is not recommended and would not yield the desired hormonal effects.
Should I Eat Bull Testicles or Other Organs On My Carnivore Diet?
Incorporating bull testicles and other organ meats into a carnivore diet may be beneficial in certain cases, but it should be approached with consideration for personal preferences and nutritional needs. Organ meats such as bull testicles are nutrient-dense and provide a range of vitamins and minerals not as abundant in muscle meats. However, their inclusion in the diet should primarily be for those who enjoy these cuts and tolerate them well.
For individuals targeting specific nutritional deficiencies, organ meats can be an excellent resource. They are rich in essential nutrients such as B folate and choline. For example, liver is an excellent source of vitamin A, which supports immune function and eye health. However, it’s important to consume these meats in proportion to the animal. Overconsumption of certain organ meats, particularly liver and kidney, can lead to vitamin A toxicity. Excessive vitamin A intake can cause serious health issues, including liver damage and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Therefore, while organ meats can be a valuable part of a carnivore diet, their consumption should be balanced and tailored to individual dietary needs. It’s crucial to listen to your body and adjust your diet accordingly. Those who do not enjoy or tolerate organ meats well should not feel compelled to include them in their diet. Instead, they can focus on other nutrient-dense animal foods that align better with their preferences and health goals. As always, variety and moderation are key components of a healthy diet, carnivore or otherwise.
Desiccated Organs vs. Fresh Organs
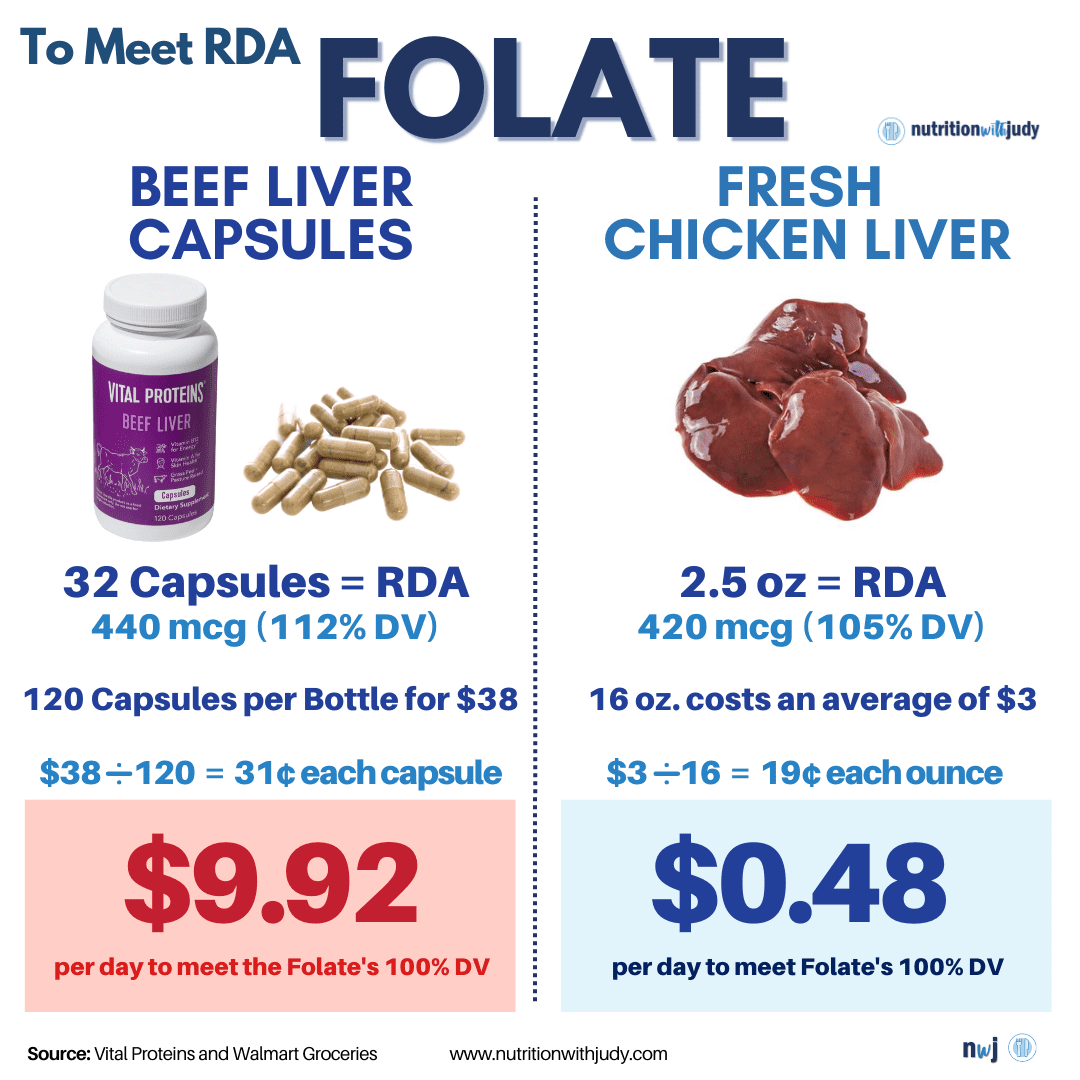

Desiccated organ supplements, while convenient, come with several concerns that should be considered before incorporating them into one’s diet. Firstly, these supplements often have a high price markup compared to fresh organ meats, making them a less economical choice. The cost-effectiveness of obtaining nutrients from fresh organs is significantly better.
Another major concern is sourcing. The quality and sourcing of desiccated organs can vary widely, and there may be issues regarding the purity and integrity of these products. It’s crucial to ensure that the organs are sourced from healthy, well-raised animals to receive the full nutritional benefits. Unfortunately, this information is not always transparent or readily available for all supplements.
Furthermore, consuming desiccated organs can bypass the body’s natural feedback system. When eating fresh organs, the body can better regulate its intake based on its current nutritional needs and satiety signals. This natural feedback mechanism is essential for preventing overconsumption and potential nutrient imbalances.
We generally recommend fresh organs for those who enjoy them and for those looking to address specific nutritional deficiencies. Fresh organ meats are not only more cost-effective but also allow for better absorption and utilization of nutrients. However, it’s important to consume these meats in moderation, particularly liver and kidney, due to the risk of vitamin A toxicity and other potential issues from excessive intake.
When purchasing organ meats, always source from the highest-quality grass-finished farms if possible. While we’ve seen many people heal eating conventional-raised, grain-finished meat, organ meat quality should really be taken into consideration.
While desiccated organ supplements offer convenience, they should be approached with caution considering factors like cost, sourcing, and the potential to disrupt the body’s natural nutrient regulation. Fresh organ meats, consumed by preference and in moderation, are generally a healthier and more balanced approach to including organ meats in the diet.
Closing Thoughts On Bull Balls
Bull testicles, commonly referred to as “Rocky Mountain oysters,” and other organ meats present a unique aspect of the carnivore diet. These organ meats are nutrient-dense, offering a range of vitamins, minerals, and high-quality protein. While they provide health benefits, such as improved mental health, autoimmune relief, and addressing certain nutritional deficiencies, their inclusion in the diet should be tailored to individual preferences and tolerances.
Preparation of bull testicles typically involves peeling, slicing, and often deep frying, leading to a tender and flavorful delicacy. However, there’s a misconception regarding their ability to significantly boost testosterone levels in humans. Consuming bull testicles does not effectively increase testosterone, as dietary testosterone is largely broken down during digestion.
Regarding organ meats like liver and kidney, caution is advised due to the risk of vitamin A toxicity from overconsumption. The balance and moderation of organ meat intake are crucial. Fresh organs are recommended over desiccated organ supplements, which can be expensive, have sourcing issues, and bypass the body’s natural feedback system. Fresh organ meats allow for better nutrient regulation and absorption.
Organ meats like bull testicles can be a beneficial addition to a carnivore diet for those who enjoy them and are aware of their nutritional impact. However, their consumption should be mindful, considering both the potential benefits and risks, and aligned with personal dietary goals and health needs.
Work With Our Trusted Carnivore Diet Functional Nutritional Therapy Practitioners
The Nutrition with Judy practice is honored to be a trusted carnivore diet practitioner support serving clients from around the globe. We’re passionate about helping our clients achieve root-cause healing in order to lead the best quality of life possible that’s nearly symptom-free. Our team is dedicated to educating our community about the incredible benefits of the carnivore diet. We welcome you to explore our free resources and are always available to support you through personalized protocols. Our Symptom Burden Assessment (SBA) is the perfect starting point for discovering your root cause and is required to work with our team— you can learn more in-depth about this powerful tool here.
Start your root-cause healing journey today and contact us any time with any questions or concerns.
DISCLAIMER: This content is for educational purposes only. While we are board-certified in holistic nutrition and are nutritional therapy practitioners, we are not providing medical advice. Whenever you start a new diet or protocol, always consult with your trusted practitioner first.