Microblog: The Body Does Not Just Run on Glucose or Ketones


Why do we only talk gluconeogenesis?
❗️There are other fatty acids than ketones.
❓Do we need glucose in the body?
Yes.
❓Does it need to come from food?
No.
🍬Here are some ways our body mechanistically uses, stores, and breaks down energy in the body for glucose (had to dig back from my board exam):
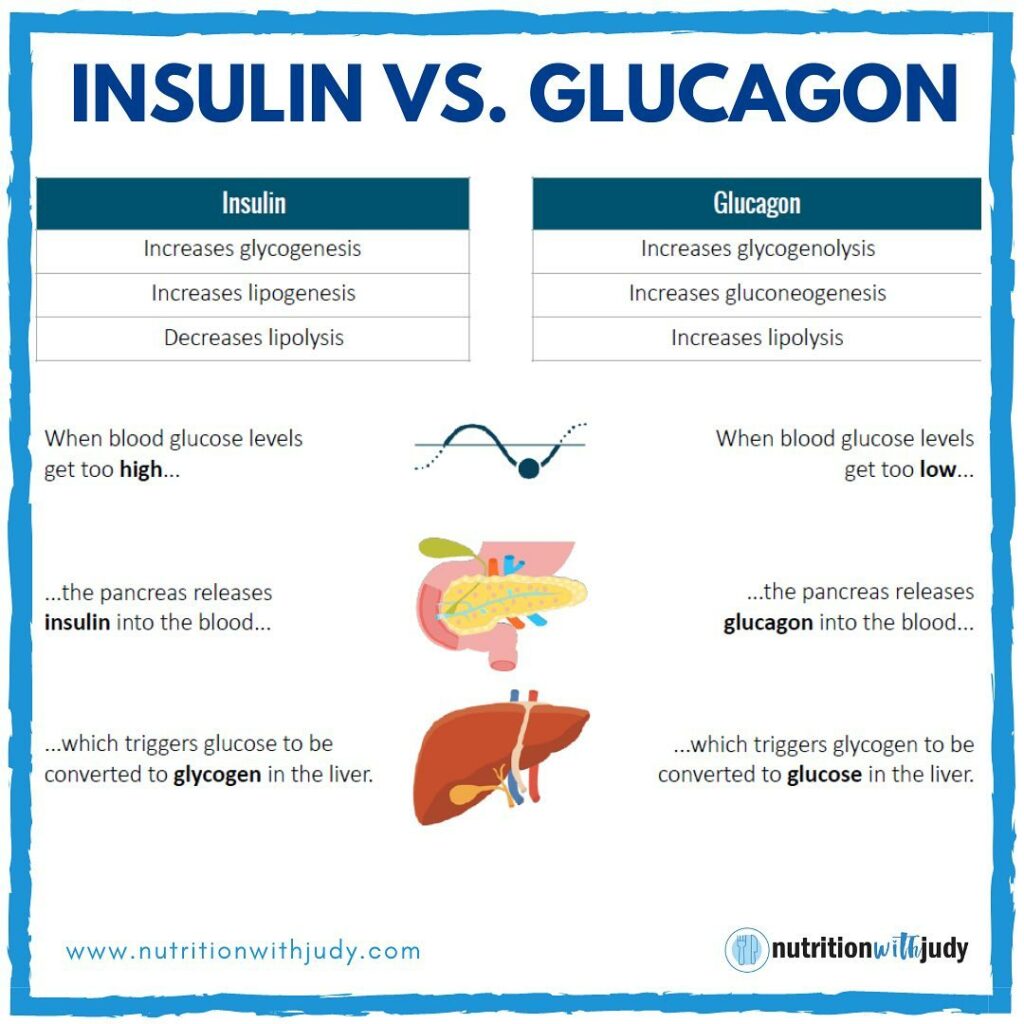
🔅GLYCOGENESIS: liver converts glucose to glycogen and stores it for future use.
💡The average adult can store about 100 gr of glycogen in the liver, about 10% of the organ’s weight. Skeletal muscle cells also convert blood glucose to glycogen (via glycogenesis), and store it locally.
💡The average adult can store about 400 gr of glycogen in the muscles, accounting for 1 to 2% of muscle mass. (glycogen stores in the muscles can only be used locally, liver glycogen can be used anywhere)
🔅LIPOGENESIS: When the liver and muscle glycogen stores are full, the liver then converts any remaining glucose to TRIGLYCERIDES, which are then stored in fat cells. (why trigs are low on a keto diet)
🔅LIPOLYSIS: The breakdown of triglycerides (stored in body fat) into GLYCEROL and free fatty acids. (When blood sugar is low, fat cells release free fatty acids into the blood)
🔅GLYCOGENOLYSIS: Converting glycogen back to glucose for energy
🔅GLUCONEOGENESIS: Protein converted to glucose within the liver (lactate, GLYCEROL, and amino acids to glucose)
🔅GLYCOLYSIS: The metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, which can then enter the Citric Acid Cycle. (Krebs)
🔅KETOGENESIS: Converting fatty acids into ketones in the liver
⛑Don’t worry about all the terms but know that there are MANY mechanisms for the body to produce glucose within the body.
🧬The body leverages insulin and glucagon hormones to pull all these energy levers (pancreas—where digestive enzymes are made).
⁉️Do you see how fat via LIPOLYSIS > GLYCEROL can ALSO be converted to glucose for energy?
💡Our body does not require an external glucose source for glucose.