Description
All tests from Nutrition with Judy include a detailed analysis (notes) that include Nutrition with Judy explanations, dietary and supplement recommendations, as well as customized next steps based on your test results.
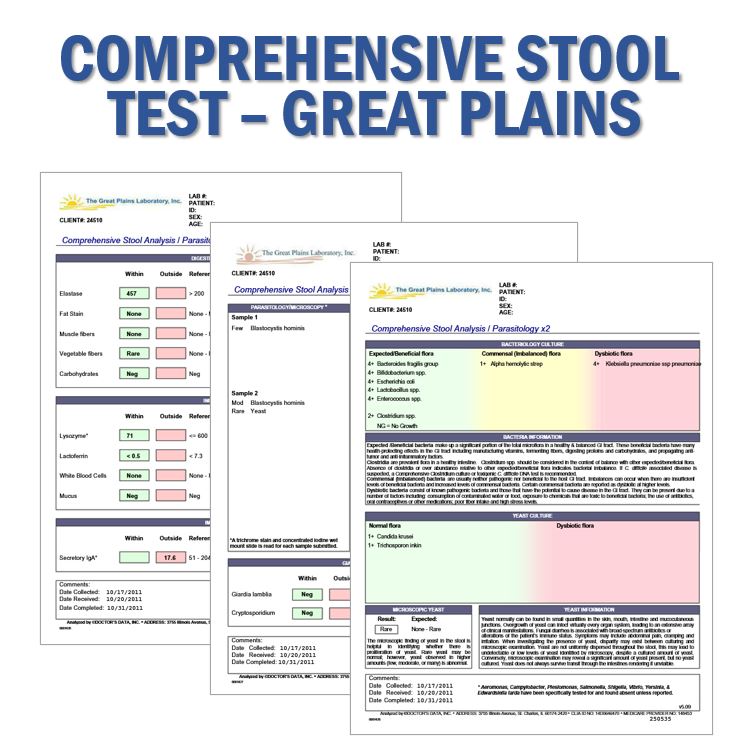
Gastrointestinal complaints are among the most common in medical care. The CSA profile helps pinpoint the causes of gastrointestinal symptoms and chronic systemic conditions, and measures key markers of digestion, absorption and inflammation. It contains comprehensive bacteriology and yeast cultures to identify the presence of beneficial flora, imbalanced flora including Clostridium species, and dysbiotic flora, as well as the detection of infectious pathogens by PCR and other gold standard methods.
Detailed Information
The Comprehensive Stool Analysis (CSA) is an invaluable non-invasive diagnostic assessment that permits practitioners to objectively evaluate the status of beneficial and imbalanced commensal bacteria, pathogenic bacteria, yeast/fungus by culture, PCR, and other gold standard methods. Precise identification of pathogenic species and susceptibility testing greatly facilitates selection of the most appropriate pharmaceutical or natural treatment agents.
Important information regarding the efficiency of digestion and absorption can be gleaned from the measurement of the fecal levels of elastase (pancreatic exocrine sufficiency), fat, muscle and vegetable fibers, and carbohydrates.
Inflammation can significantly increase intestinal permeability and compromise assimilation of nutrients. The extent of inflammation, whether caused by pathogens or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can be assessed and monitored by examination of the levels of biomarkers such as calprotectin, , lactoferrin, and lysozyme via this stool test. These markers can be used to differentiate between inflammation associated with potentially life-threatening inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which requires lifelong treatment, and less severe inflammation that can be associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) which is frequently due to the presence of enteroinvasive pathogens. Calprotectin and lactoferrin are only markedly elevated prior to and during the active phases of IBD, but not with IBS. Monitoring these levels in patients with IBD can therefore facilitate timely treatment of IBD, and can be ordered separately. Since the vast majority of secretory IgA (sIgA) is normally present in the GI tract, where it prevents binding of pathogens and antigens to the mucosal membrane, it is essential to know the status of sIgA in the gut. sIgA is the only bona fide marker of humoral immune status in the GI tract.
Cornerstones of good health include proper digestion of food, assimilation of nutrients, exclusion of pathogens and timely elimination of waste. To obtain benefits from food that is consumed, nutrients must be appropriately digested and then efficiently absorbed into portal circulation. Microbes, larger-sized particles of fiber, and undigested foodstuffs should remain within the intestinal lumen. Poor digestion and malabsorption of vital nutrients can contribute to degenerative diseases, compromised immune status and nutritional deficiencies. Impairment of the highly specific nutrient uptake processes, or compromised GI barrier function, as in “leaky gut syndrome,” can result from a number of causes including:
- Low gastric acid production
- Chronic maldigestion
- Food allergen impact on bowel absorptive surfaces
- Bacterial overgrowth or imbalances (dysbiosis)
- Pathogenic bacteria, yeast or parasites and relate dtoxic irritants
- The use of NSAIDs and antibiotics
Impairment of intestinal functions can contribute to the development of food allergies, systemic illnesses, autoimmune disease, and toxic overload from substances that are usually kept in the confines of the bowel for elimination. After performing a stool test, efficient remediation of GI dysfunctions incorporates a comprehensive guided approach that should include consideration of elimination of pathogens and exposure to irritants, supplementation of hydrochloric acid, pancreatic enzymes and pre- and probiotics, and repair of the mucosal barrier.
NOTE: The Comprehensive Stool Analysis does not include analysis for parasites. For a stool test that includes testing for parasites, consider: Complete GI Map Stool Test
The Importance of the Comprehensive Stool Analysis
Many chronic disorders result from digestive problems and inadequate nutrient absorption. Even with a very complete and balanced diet, nutrients have to be properly digested to transport vitamins to different parts of the body. Proper gastrointestinal functioning also ensures elimination of toxic molecules, microbes and undigested food particles from the body, which helps prevent infections, toxic reactions, allergies, and other health problems.
The role of abnormal intestinal microorganisms in gastrointestinal disorders is widely known. However, research also shows the relationship between the gastrointestinal and other systems in the body, such as the neurological, hepatic, and immune systems. For example, excessive yeast produces toxic metabolites, which can pass through the blood-brain barrier and alter neurological functioning, causing “brain fog,” behavior problems, and learning difficulties. Exposure to certain pathogens can cause the formation of antibodies that can interfere with the brain in predisposed individuals, causing problems with motor function. Excess of toxic by-products of certain bacteria can interfere with neurotransmitters and cause fatigue. Beneficial bacteria, on the other hand, helps with vitamin absorption and infection prevention.
Comprehensive Stool Evaluation Will Give You Specific Information About The Following Digestive Criteria:
- Digestion of nutrients (chymotrypsin, triglycerides, muscle fibers, vegetable fibers)
- Absorption of nutrients (cholesterol, carbohydrates, steatocrit %)
- Elimination efficiency of undigested food residues and toxins
- Levels of healthy bacterial flora versus potentially pathogenic bacteria species, yeast, and parasites
- Culture and sensitivities of pathogenic yeast and bacteria
- Infectious pathogens (EIA evaluation for Campylobacter, Enterohemorrhagic E.coli cytotoxin, Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium)
- Indices and markers of intestinal immune function (fecal sIgA)
- Indices and markers of inflammation (lysozyme and lactoferrin levels)
- Indices and markers of intestinal physiology and of intestinal health (presence of RBC, WBC, mucus, occult blood, fecal pH, and short-chain fatty acids analysis)
About the Test
The Comprehensive Stool Analysis detects the presence of pathogenic yeast, parasites, and bacteria, which could be contributing to chronic illness and neurological dysfunction. It provides information about prescription and natural products that may be effective against specific microorganism strains detected in the sample. The test also evaluates beneficial bacteria levels, intestinal immune function, overall intestinal health (presence of occult blood, short-chain fatty acids analysis, pH, mucus, and other criteria), and markers for inflammation.
This test purchase also comes with Nutrition with Judy notes and diet/supplemental protocol per the test results.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.